How to Undervolt CPU in BIOS 2025
To undervolt the CPU in BIOS, access the BIOS settings and tweak the voltage settings for optimal performance and temperature management.
Undervolting your CPU through the BIOS can provide benefits such as reducing power consumption, improving overall system stability, and minimizing heat generation.
By adjusting the voltage levels, you can optimize the CPU’s performance without sacrificing its lifespan.
Undervolting is particularly useful for overclockers looking to enhance their CPU’s capabilities while keeping temperatures under control.
We will discuss the step-by-step process of undervolting your CPU in the BIOS, providing you with a comprehensive guide to ensure successful undervolting and maximum efficiency for your system.
Follow these instructions to unlock the potential of your CPU while maintaining optimal thermal conditions.
Credit: www.youtube.com
Understanding The Basics Of Cpu Undervolting
Learn the basics of CPU undervolt and how to undervolt your CPU in the BIOS with this comprehensive guide.
Adjusting your CPU’s voltage can improve performance and reduce heat generation for a more efficient system.
Discover the step-by-step process to optimize your CPU’s power consumption through BIOS settings.
Undervolting is a process where you reduce the voltage supplied to your CPU, resulting in lower power consumption and reduced heat generation.
This technique allows you to optimize your CPU’s performance while maintaining stability. In this section, we will explore the concept of CPU undervolting and its benefits.
What Is CPU Undervolting And Why Is It Useful?
- CPU undervolting involves reducing the voltage supplied to the processor, which allows it to operate at lower power levels.
- This technique is useful for achieving better power efficiency and reducing heat generated by the CPU.
- Undervolting can result in improved performance and longevity by reducing the risks associated with high temperatures.
The Impact Of High Cpu Temperatures On Performance And Longevity
- High CPU temperatures can negatively impact the overall performance of your system.
- Excess heat can throttle the CPU, causing it to slow down and potentially resulting in performance issues.
- Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can also reduce the lifespan of your CPU.
Benefits Of Undervolting In Terms Of Power Consumption And Heat Reduction
- Undervolt reduces power consumption, resulting in lower electricity bills and increased battery life for laptops and mobile devices.
- By lowering the CPU voltage, undervolting can effectively reduce heat generation, enabling your system to run cooler.
- Cooler temperatures can lead to improved stability and performance, especially during demanding tasks such as gaming or video rendering.
Undervolting your CPU is a valuable technique that can optimize performance, improve power efficiency, and reduce heat generation.
In the next sections, we will delve deeper into the step-by-step process of undervolting in BIOS and discuss the precautions to keep in mind.
Stay tuned!
Preparing Your Computer For Undervolting
Ensure optimal performance by properly preparing your computer for undervolting.
Discover how to undervolt the CPU in the BIOS to enhance efficiency and reduce power consumption for remarkable results.
Undervolting your CPU can be an effective way to reduce power consumption and temperature, thereby optimizing the performance of your computer.
However, before you venture into the world of undervolt, it is important to ensure that your motherboard supports this feature and to consider a few important factors.
Additionally, having the necessary tools and software for undervolting in BIOS is crucial. In this section, we will cover these aspects in detail.
Ensure Your Motherboard Supports CPU Undervolting:
- Check your motherboard specification: Before you start the undervolting process, it is essential to verify whether your motherboard supports CPU undervolt. Check the manufacturer’s website or the user manual of your motherboard for this information.
- Look for BIOS options: Access your BIOS settings by restarting your computer and pressing the designated key (usually Del or F2) during startup. Once in the BIOS, look for options like “Voltage Control” or “CPU Voltage” under the relevant menus. If you can find these options, it indicates that your motherboard supports CPU undervolting.
Important Considerations Before Starting The Undervolting Process:
- Research your CPU: Every CPU model has its own specific characteristics, and it’s important to have a clear understanding of your CPU’s default voltage range and optimal operating temperatures. Research the optimal voltage range for your CPU and gather relevant information about undervolting considerations specific to your CPU model.
- Understand the risks: Undervolt, though generally safe when done correctly, carries some risks. It is important to be aware that a significant undervolt can potentially lead to system stability issues, including crashes and instability. Additionally, undervolting beyond a safe threshold can cause data corruption or even permanent damage to your CPU.
- Make a backup: Before making any changes to your BIOS settings, it is recommended to back up your important data. Although the risk of data loss during undervaluations is low, it’s always better to be safe than sorry.
Necessary Tools And Software For Undervolting In Bios:
- BIOS access: Undervolting is performed within your computer’s BIOS settings. Ensure that you have the necessary information to access your BIOS by referring to your motherboard’s manual or contacting the manufacturer if needed.
- CPU monitoring software: To monitor the effects of your undervolt in real time, it is essential to have CPU monitoring software installed. Software options like HWiNFO, Core Temp, or CPU-Z provide accurate real-time information about CPU temperature, voltage, and other important parameters.
- Stress testing software: After making adjustments to your CPU voltage, it is vital to test the stability of your system. Stress testing software like Prime95, AIDA64, or IntelBurnTest can help you assess the stability by subjecting your CPU to intense workloads for an extended period of time.
By ensuring that your motherboard supports CPU undervolting, considering important factors before starting the process, and having the necessary tools and software at your disposal, you will be well-prepared to embark on your undervolting journey in the BIOS.
Remember to proceed with caution, following expert recommendations and constantly monitoring your CPU’s performance throughout the process.
Step-By-Step Guide To Undervolting CPU in Bios
Learn how to undervolt your CPU in the BIOS with this step-by-step guide.
Optimize your computer’s performance and reduce power consumption by following these simple instructions.
Accessing The Bios On Your Computer:
- Turn on your computer and immediately press the designated key to access the BIOS. This can differ depending on your computer manufacturer, but common keys include F2, F10, or Del.
- Once you’re in the BIOS, navigate to the “Settings” or “Configuration” menu using the arrow keys on your keyboard. Look for options related to power management or CPU settings.
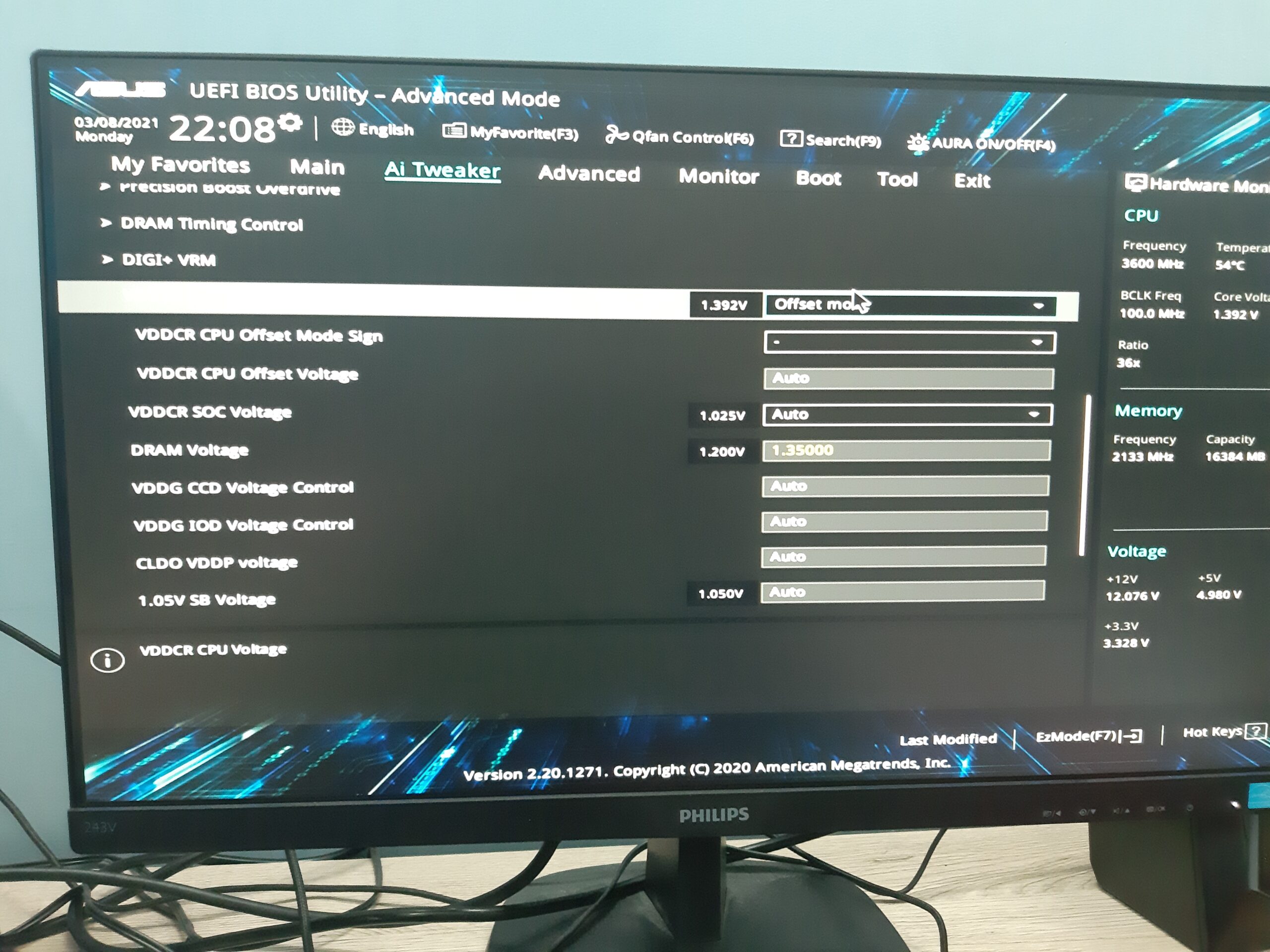
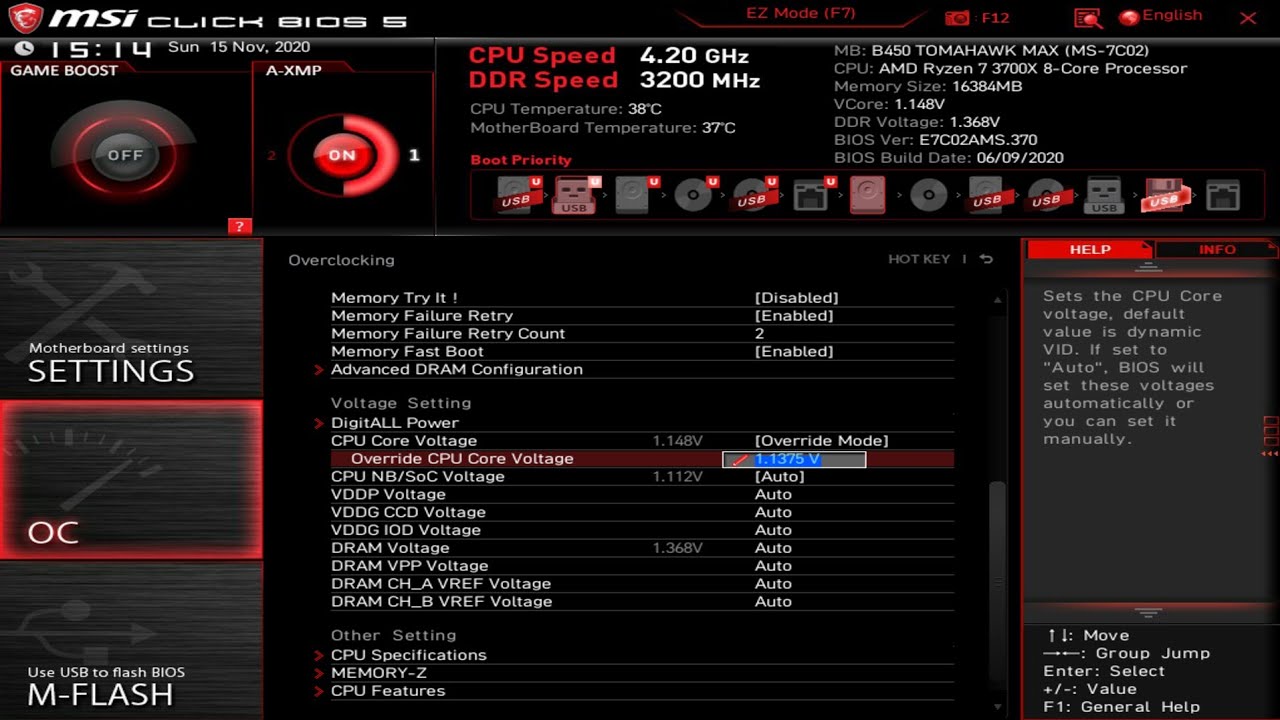
Locating The CPU Undervolting Settings In Bios:
- In the BIOS menu, find the section related to CPU settings or advanced power management options.
- Look for terms like “voltage”, “CPU voltage”, or “voltage control”. It may be located under submenus such as “Performance”, “Power”, or “Advanced”.
Adjusting The CPU Voltage Settings For Undervolting:
- Once you’ve located the CPU voltage settings, select the option to modify the values.
- Lower the CPU voltage gradually by small increments, such as 0.01V or 0.05V, to reduce the risk of instability.
- Make sure to save your changes before exiting the BIOS.
Understanding The Relationship Between Voltage And Stability:
- Undervolt reduces the amount of voltage supplied to the CPU, which can result in lower power consumption and temperatures.
- However, insufficient voltage can cause instability or crashes. It’s essential to find the right balance between voltage reduction and system stability.
Testing And Monitoring Your Undervolted CPU for Stability And Performance:
- Use stress-testing software such as Prime95 or IntelBurnTest to assess the stability of your undervolted CPU.
- Monitor the CPU temperature and performance during the stress test to ensure it remains within safe limits.
- If instability issues arise, gradually raise the voltage until stability is achieved, keeping an eye on temperatures.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can successfully undervolt your CPU in the BIOS. Undervolt can help improve power efficiency, reduce heat output, and potentially increase the lifespan of your CPU.
Remember to proceed with caution and monitor stability during the process.
Advanced Tips And Troubleshooting
Learn advanced tips and troubleshooting techniques for undervolting your CPU in the BIOS. Optimize performance and reduce power consumption with these step-by-step instructions.
Undervolting your CPU in the BIOS can be an effective way to optimize its performance and stability.
However, it’s crucial to approach this process with caution and follow the necessary precautions.
In this section, we will explore some advanced tips and troubleshooting techniques to help you fine-tune your voltage settings, understand the potential risks, and overcome common issues that may arise during the undervolting process.
Fine-Tuning Voltage Settings To Achieve Optimal Performance And Stability:
- Start with small adjustments: Begin by making minor changes to the voltage settings, reducing the voltage in small increments, such as 0.010V. This approach allows you to find the optimal balance between performance and stability.
- Monitor the temperatures: After applying voltage changes, closely monitor the CPU temperatures during stress tests or heavy usage scenarios. The purpose is to ensure that the undervolt adjustments do not lead to excessive overheating. If the temperatures become too high, consider reverting the changes or adjusting other settings, such as fan curves or cooling solutions.
- Test for stability: Stability is a critical factor when undervolting your CPU. You can examine the stability by conducting stress tests or running resource-intensive tasks for an extended period. If you experience system crashes, freezes, or blue screens, it indicates instability. In such cases, slightly increase the voltage until the system becomes stable again.
- Find the sweet spot: Achieving the ideal balance between voltage reduction and performance can be a trial-and-error process. Experiment with different voltage levels and observe the performance impact. You may discover a point where the CPU operates at a lower voltage without compromising its performance and stability.
- Document your settings: It is essential to document each adjustment you make during the undervolting process. In case you encounter any issues or need to revert to earlier settings, having a record of the changes can prove valuable.
Potential Risks And Precautions When Undervolting Cpu:
- Voiding warranty: Undervolting your CPU, if done incorrectly, can potentially void your warranty. Always review your CPU manufacturer’s warranty terms and conditions before making any modifications to voltage settings.
- System instability: Excessive undervolting can lead to system instability, resulting in crashes, blue screens of death (BSODs), and data loss. It is crucial to strike the right balance between undervolt and stable operation.
- Data corruption: In extreme cases of undervolt, data corruption may occur, potentially leading to the loss of valuable files or important system data. Regularly back up your data to mitigate this risk.
- Incompatibility with certain applications or hardware: Some applications or hardware components might be sensitive to undervolt. If you experience issues with specific software or peripherals after undervolting, it is advisable to revert to default voltage settings.
Troubleshooting Common Issues During The Undervolting Process:
- Resetting the BIOS: If you encounter significant stability issues, you can try resetting the BIOS settings to their default values. This action can help eliminate any unintended or faulty voltage adjustments.
- Incremental voltage adjustments: If stability issues persist, consider gradually increasing the voltage until stability is restored. This step may reduce the extent of undervolt but can help find a more reliable and balanced configuration.
- Updating BIOS firmware: Outdated or incompatible BIOS firmware can cause complications when undervolting. Check for any available BIOS updates from your motherboard manufacturer and apply them if necessary.
- Consulting forums and communities: If you encounter specific issues during the undervolting process, consulting online forums or communities dedicated to overclocking and undervolting can provide valuable insights and potential solutions.
Remember, undervolting your CPU requires careful consideration, monitoring, and adjustment.
If you are unsure of any steps or lack experience with BIOS settings modifications, it is advisable to seek guidance from tech-savvy communities or professionals before proceeding.
Recommended Tools And Software For CPU Undervolting
Discover the recommended tools and software to effectively undervolt your CPU in the BIOS, optimizing performance and reducing power consumption.
Gain insights into the step-by-step process of undervolting and improving your system’s efficiency.
Undervolting your CPU in the BIOS can be a great way to optimize performance, reduce heat output, and increase your laptop’s battery life.
However, it’s important to have the right tools and software to ensure a smooth and successful undervolting process.
In this section, we’ll explore some popular tools and software options available for CPU undervolting, discussing their features, benefits, and recommendations for choosing the right one.
Overview Of Popular Tools And Software Available For CPU Undervolting:
- ThrottleStop: This widely-used tool provides advanced control over CPU voltage, frequency, and power settings. With features like Turbo Boost disabling and temperature monitoring, ThrottleStop offers a comprehensive solution for undervolting and optimizing CPU performance.
- Intel XTU: Developed by Intel, this software allows users to adjust voltage and frequency settings for Intel processors. Intel XTU comes with a user-friendly interface and includes features like stress testing and benchmarking to ensure stability and performance gains.
- AMD Ryzen Master: Specifically designed for AMD Ryzen processors, this software provides precise control over CPU voltage and frequency settings. It offers real-time monitoring, integrated overclocking, and tuning capabilities, making it an excellent choice for Ryzen users.
Features And Benefits Of Each Tool/Software:
- ThrottleStop:
- Allows fine-grained control over CPU voltage, frequency, and power settings.
- Disables Turbo Boost for improved efficiency and reduced heat output.
- Monitors CPU temperature to prevent overheating.
- Offers undervolting profiles for different usage scenarios, maximizing performance while minimizing power consumption.
- Intel XTU:
- User-friendly interface with easy-to-use controls.
- Ability to adjust voltage and frequency settings for Intel processors.
- Includes stress testing and benchmarking features for stability and performance testing.
- Provides real-time monitoring of CPU temperature, power, and utilization.
- AMD Ryzen Master:
- Tailored specifically for AMD Ryzen processors.
- Offers precise control over CPU voltage and frequency settings.
- Integrated overclocking functionality to push performance limits.
- Real-time monitoring of vital statistics like temperature and clock speeds.
Recommendations And Best Practices For Choosing The Right Tool/Software:
- Consider your specific CPU brand and model: Ensure that the tool or software you choose is compatible with your CPU.
- Evaluate the features and functionality: Look for tools that offer the necessary features like voltage control, frequency adjustment, and real-time monitoring.
- User-friendly interface: Opt for software that provides a straightforward interface and intuitive controls for ease of use.
- Stability and support: Choose tools that have a good reputation for stability and ongoing support to ensure a smooth undervolting experience.
Undervolting your CPU can bring significant benefits to your system, but it’s important to select the right tools and software. ThrottleStop, Intel XTU, and AMD Ryzen Master are among the popular options available, each offering unique features and benefits. Assessing compatibility, functionality, and ease of use will help you make an informed decision to optimize your CPU’s performance while maintaining stability.
Real-World Examples And Success Stories
Discover real-world examples and success stories on how to undervolt CPU in BIOS. These practical case studies provide valuable insights and step-by-step guidance to optimize your computer’s performance efficiently and effectively. Master the art of undervolting and unleash the true potential of your CPU.
Stories Of Users Who Have Successfully Undervolted Their Cpus:
- User A: One user shared their success story of undervolting their CPU in the BIOS. They noticed their CPU was running hot and causing performance issues. After some research, they decided to try undervolting as a solution. With careful tweaking of voltage settings, they were able to lower the CPU temperature significantly without any negative impact on performance. They reported smoother multitasking and reduced fan noise.
- User B: Another user shared their experience of undervolting their CPU in the BIOS. By undervolting, they were able to optimize power consumption and lower heat output. This resulted in better overall system stability and reduced thermal throttling during heavy tasks. Their CPU temperatures dropped by a noticeable margin, leading to improved performance during demanding applications and smoother gameplay.
- User C: An enthusiastic user documented their successful journey of undervolting their CPU in the BIOS. They noticed their CPU was running at high temperatures, causing frequent thermal throttling and performance drops. Through careful undervolting adjustments, they were able to stabilize their CPU temperatures and eliminate heat-related throttling. As a result, they experienced a significant boost in performance, particularly during resource-intensive tasks like video editing and gaming.
Performance Improvements And Benefits They Experienced:
- Improved thermals: Undervolting the CPU in the BIOS helped users decrease the operating temperature. This resulted in more consistent and lower CPU temperatures during heavy workloads, reducing the risk of thermal throttling and improving overall system stability.
- Enhanced performance: Users reported improved performance after undervolting their CPUs. With lower temperatures, the CPU was able to maintain higher clock speeds for longer periods, resulting in faster and more efficient processing. This led to smoother multitasking, faster application load times, and improved gaming performance.
- Power efficiency: Undervolting allowed users to optimize their CPU’s power consumption. By reducing the voltage supplied to the CPU, they achieved increased power efficiency without sacrificing performance. This meant lower electricity bills and less strain on the system’s power supply.
Lessons Learned And Tips From Their Experiences:
- Start conservative: When undervolting your CPU, it’s advisable to start with conservative voltage adjustments. Gradually decrease the voltage in small increments and test stability and performance after each adjustment. This approach minimizes the risk of instability or crashes.
- Monitor for stability: After making voltage adjustments, closely monitor your system for any signs of instability, such as crashes or errors during stress tests or demanding tasks. If stability issues occur, consider slightly increasing the voltage until stability is achieved.
- Individual results may vary: Undervolting success depends on various factors, including CPU architecture, cooling solution, and specific workload demands. It’s essential to understand that while undervolting can often bring positive results, individual experiences may vary.
- Documentation and backups: Keep a record of your voltage adjustments and any changes made in the BIOS. This documentation can help troubleshoot any instability issues that may arise. Additionally, consider backing up your BIOS settings before making any adjustments to easily revert changes if necessary.
- Research your CPU: Before undervolting, research the specific CPU model to learn about others’ experiences and recommended voltage ranges. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of your CPU can ensure a more successful undervolting process.
Remember, undervolting CPUs carries some level of risk, and it’s essential to proceed with caution. If you’re unsure about the process or its implications, it’s recommended to seek guidance from experienced users or consult the manufacturer’s documentation.
FAQs for How to Undervolt CPU in Bios
Is It Safe To Undervolt Cpu Bios?
Undervolting CPU BIOS can be safe, but caution is necessary to avoid potential instability issues.
How To Undervolt 5800X3D From Bios?
To undervolt your 5800x3d from BIOS, follow these steps: 1. Access the BIOS settings on your computer. 2. Locate the section related to voltage control or CPU settings. 3. Adjust the voltage settings for your 5800x3d, lowering it to achieve the desired undervolting.
4. Save the changes and exit the BIOS. 5. Monitor your CPU’s performance and stability after undervolting to ensure optimal results.
How To Safely Undervolt A CPU?
To safely undervolt a CPU, follow these steps: 1. Research and understand your CPU’s voltage limits and specifications. 2. Use a reliable software tool to gradually reduce the voltage in small increments. 3. Monitor the temperature and stability of your CPU while testing for optimal performance.
4. Make sure to stress test your CPU after undervolting to ensure it can handle heavy workloads without issues.
Why Did Intel Stop Undervolting?
Intel stopped undervolting due to issues with CPU stability and potential damage to processors.
Conclusion
Undervolting your CPU in the BIOS can be a highly effective way to optimize your system’s performance without compromising stability.
By lowering the voltage supplied to your CPU, you can reduce power consumption and heat generation, leading to improved efficiency and potentially longer lifespan for your processor.
However, it’s important to approach undervolting with caution and ensure you have a good understanding of your specific CPU’s capabilities and limitations.
If done incorrectly, undervolting can result in instability and potential damage to your hardware.
Before making any changes, it’s advisable to research extensively, consult reliable sources, and consider seeking guidance from experienced users or professionals.
With the right knowledge and care, undervolting can be a valuable technique for optimizing your CPU’s performance and enhancing your overall computing experience.